Zinc nickel rechargeable batteries have similar discharge characteristics to alkaline batteries. The open circuit voltage is significantly higher than the nominal voltage, but for most of the working time, the discharge voltage remains near the nominal voltage. When there is not much remaining power, there will be a significant drop in voltage.
Initial stage: When discharging begins, there may be a slight decrease in battery voltage due to instantaneous voltage drop caused by internal impedance.
Steady stage: Subsequently, a longer plateau period is entered, during which the battery voltage remains relatively stable. This is an advantage of zinc nickel batteries, as they can provide consistent power to the device for most of its usage time.
End stage: As the battery approaches its capacity limit, the voltage will rapidly decrease. This is due to the consumption of active substances and an increase in internal resistance. This rapid decline stage is a signal that the battery needs to be recharged.
Cut off voltage: In order to protect the battery from excessive discharge and extend its lifespan, it should be stopped from use or charged before reaching the manufacturer’s recommended minimum operating voltage.
Please note that the actual discharge curve may also be affected by factors such as temperature, discharge current, and battery aging. For example, high current discharge can lead to steeper voltage drops and lower overall capacity; Low temperature conditions can also reduce battery performance.
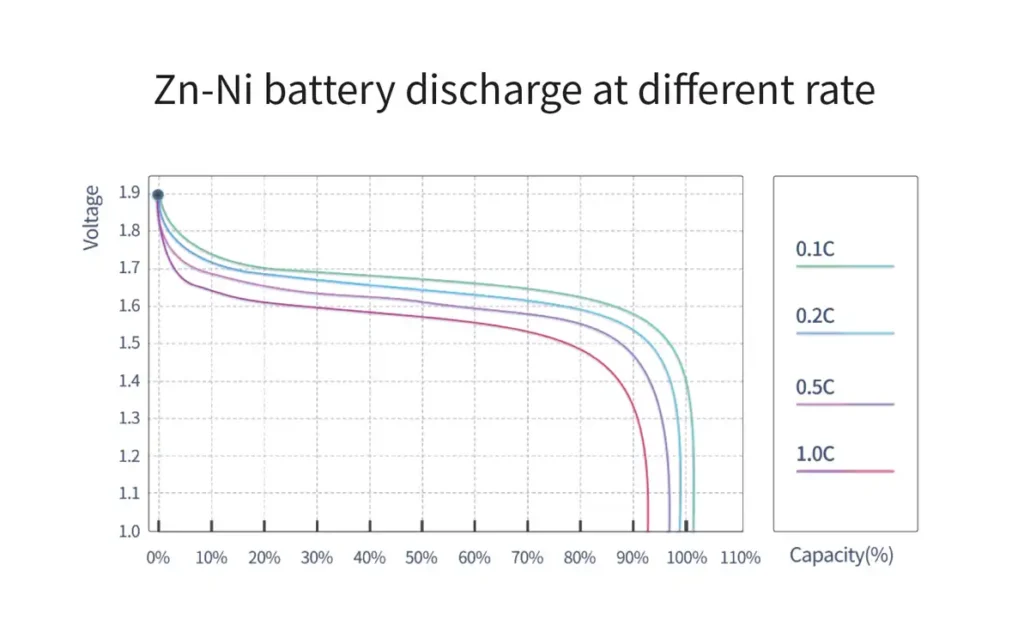
The discharge curve of zinc nickel rechargeable batteries shows the variation of voltage with time or discharge capacity during the discharge process. This type of battery typically has a relatively flat discharge curve, which means they can provide a relatively stable output voltage throughout the entire discharge cycle.




